Variables in C - Programming Language
Learn about the Variables type , convention and best practises in C programming language
Variables
Variables are the name of a memory location where data is being stored .
int a = 10 ;
Here we are storing the value 10 in a variable named a.
How to visulaise a variable in a place .
We can imagine a variable as a
conatinerin any language where we can store some data and modify that in later down the line in code .A variable make it easy for us to access the data we want to access for
mathematical operations.
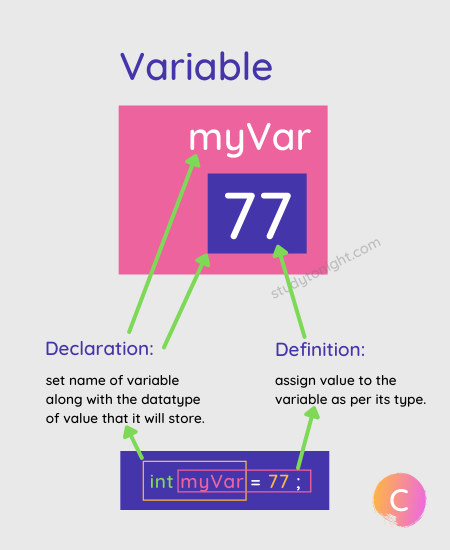
Lets take an example for better undersatnding :
lets assume that i want to add some numbers in my c program and then print the result in terminal .
int i = 10; int j = 20; // int k = i + j; printf("%d", i + j);When we run the code and its print the output we get our result , but here we are not able to
store that datainto something for later use .So we need to store the result in a
variable.
Rules for naming variables .
So there are bunch of rules and regulations for naming variables , that one should follow otherwise the compiler will give an error .
Variables should start with a letter or an underscore ("_").It means that if we start the variable name with a number then the compiler will give an error. we can make variable name as "_abc" or "abc_" or "abc" but not "1abc" or "@abc" or "abc@" .
Variables should not contain spaces or commas.It means that if we have a variable name which contains spaces then the compiler will give an error. we can make variable name as "abc1def" or "abc_def" or "abcdef" but not "abc,def" or "abc def" or "abc@def" .
Variables should not start with a number.It means that if we start the variable name with a number then the compiler will give an error. we can make variable name as "abc" or "abc_" or "abc" but not "1abc" or "45abc" or "001_abc@" .
Variables should not contain any special characters only "_" is allowed .It means that if we have a variable name which contains special characters then the compiler will give an error. we can make variable name as "abc" or "abc_" or "abc" but not "1abc" or `@abc` or "abc@" .
How to declare a variable .
- We can declare a variable in two ways .
- One is by using the keyword
int. - Another is by using the keyword
float. - we can also use the keyword
char. - we can also use the keyword
double. - All these keywords are used to declare a
variable.
Lets take an example for better undersatnding :
int i = 10;
float f = 10.5;
char c = 'a';
double d = 10.5;
- Here we are declaring a variable named
iand assigning it the value 10 . Here we are declaring a variable named
fand assigning it the value 10.5 .Here we are declaring a variable named
cand assigning it the value 'a' .
Here all these i , f , c , d are called variables .
- Here all these int , float , char , double are called
typesof the variable and the type of data they can store ,Datatypes.
we would be discussing datatypes in next Module !
How to assign a value to a variable .
- We can assign a value to a variable by using the keyword
=. datatype variable_name = value_to_be_stores ;
Naming Convention
There are some convention for naming variables . By following these convention we can make our code more readable and maintainable. Some of the convention are as follows:
Variable names should be written in lowercase_with_underscore.Variable names should not start with a number.Variable names should not contain any special characters.Variable names should not contain spaces.one should mantain a naming system for the variables so that with just one look we can find the variabl, and predict here the value is comming from.
```c
int a = 10; ❎
// here we are assigning the value 10 to the variable a , but with more code and more complexity we shall not be able to find the origin of a , and this can take a much time in debugging the code .
int number = 10; ✅
// here by just looking at the variable we can make a idea about the origin of the variable number that its store some kind of number .
int random_number = 10004546679667677;
// here we can see that the variable `10004546679667677` is comming from the `random_number` variable.
int user_name = "Abhishek Kushwaha";
// here we can see that the variable `Abhishek Kushwaha` is comming from the `user_name` variable.
int user_age = 20;
// here we can see that the variable `20` is comming from the `user_age` variable.
```

